
Introduction
XLAW® is a technological and methodological invention conceived and implemented to experiment, for the first time in Italy, an innovative approach to Urban Security problems which is based on the possibility of being able to prevent, according to the logic of forecasting, the phenomena of widespread illegality which normally take place in our beautiful cities.The invention as a whole consists of a technical and methodological protocol configured to generate and strategically use georeferenced predictive alarms of possible crimes, processed according to an exclusive Deep Learning forecasting model.
The innovation consists in the fact that compared to all the traditional control systems (video surveillance etc.) or alarm systems (intrusion detection, electronic barriers etc.) which have the limitation of being able to be considered only after the crimes have occurred, the invention allows to prevent them by supervising where it is scientifically foreseen that they happen and not where it is thought they could happen or worse, where they have already happened, the well-known limitation of the traditional method of prevention.
The long and widespread experimentation of the invention, conducted to make a valid contribution to knowledge and progress in the fight against widespread illegality, can be considered as a whole a scientific research whose results have been evaluated and validated independently by the most important security structures and by two universities thanks to which, it was possible to establish that Artificial Intelligence, now increasingly alongside human activities, if implemented and used appropriately also for purposes of Urban Security, given the high reliability and precision of the analyzes and therefore of the strategic information that it manages to provide, can elevate the prevention and control activity and make it more dynamic, precise and effective, avoiding the waste of resources and energy.
«Its long use has moved the strategic construct of the control action from a restorative vision of the damage to a vision probabilistic risk, therefore from a run-up logic of the problems and the effects that they generate typical of the permanent emergency, to one who works on the schemes of prevention "(Prof. Giacomo Di Gennaro Department of Political Sciences Director of the II level Master Criminology and Criminal Law Criminal Analysis and Policies for the Urban Security Federico II University of Naples)
Experimentations
2004/2019
 Police Department Napoli, Salerno, Prato, Venezia, Parma e Modena.
Police Department Napoli, Salerno, Prato, Venezia, Parma e Modena.
Awards
2018
 Finalist and winner of the SMAU Digital Innovation Award.
Finalist and winner of the SMAU Digital Innovation Award.
Validations
2019
 Department of Public Security Central Anti-Crime Directorate.
Department of Public Security Central Anti-Crime Directorate.
2017/2019
 Federico II University Department of Political Sciences - Parthenope University Department of Business and Economic Studies.
Federico II University Department of Political Sciences - Parthenope University Department of Business and Economic Studies.
2022
 Ministry of Economic Development - Directorate General for the Protection of Intellectual Property - Patent and Trademark Office.
Ministry of Economic Development - Directorate General for the Protection of Intellectual Property - Patent and Trademark Office.
Honors
2014
 Best practice recognized within the European project BESECURE and S.E.L.P.E of the Giancarlo Siani foundation.
Best practice recognized within the European project BESECURE and S.E.L.P.E of the Giancarlo Siani foundation. Genesis, evolution and results
The research, development and experimentation project of the invention kicks off following a twenty-year study on the phenomena of urban deviance which has made it possible to distinguish with greater precision the widespread illegality in the cities and to understand that thefts, robberies, bag-snatching, pickpocketing, scams and other crimes, have cyclical and permanent characteristics and can be foreseen if it is possible to define an appropriate forecasting logic and transfer it to a machine learning model (Deep Learning) which, on the basis of certain information on criminal phenomena and on the dynamics social situations in the contexts in which they occur, has the task of decoding the criminal design at the origin of the individual crimes, foreseeing their reconfiguration in time and space, with the aim of creating the optimal condition to be able to prevent them more effectively than with the traditional method.The result of years of multidisciplinary study, the model is based on an advanced analysis method never applied before to analyze and deal with criminal risk and which surpasses all approaches known so far such as that of crime linking, probabilistic calculation and paper processing topography of areas with the highest criminal incidence (hot spots) which present gray areas and critical issues of an ethical and functional type.
The experimentation of the invention by several security structures conducted with the contribution of two universities for the independent supervision of the work, has made it possible to transparently establish that basing the activities on the selectivity and sequentiality of the controls by virtue of the predictive processing according to the model of Artificial Intelligence, it is possible to prevent crimes more effectively than the traditional method and rationalize resources and energies avoiding their waste.
Through an articulated framework, the invention was introduced for independent experimentation in operational security divisions of various Italian cities and used according to an exclusive protocol to facilitate its easier and more correct application. With the aim of trying to improve the crime prevention activity in urban areas according to the different paradigm, given by the possibility of being able to prevent offenses by predicting them thanks to Artificial Intelligence, controls on the territory have been set up in a selective and sequential manner and therefore with dynamic precision and punctuality with respect to the real degree of evolution of the risk. The operational support of Artificial Intelligence has allowed operators to acquire, in symbiosis with it, greater risk awareness and decision-making ability directly in the operational scenario and to participate proactively in an appropriate "risk assessment" strategy that goes beyond the limit of having to work only on the emergency or on the basis of empirical or obsolete analyzes and evaluations.
The results obtained are not accidental because they are situated in that progressive itinerary which can be found in the copious literature on the dynamics of deterrence in Game Theory. In fact, many studies dedicated to this topic show that for these crimes the punishment of the offender should not be the first objective to be pursued, because the attempt to inflict punishment is random, expensive and produces poor results. What should be more valued in the daily dispute with the offender, is instead deterrence because in fact it is a penalty that severely limits the criminal plan and therefore the efforts should be greater to get to inflict it systematically. In fact, if potential offenders are sufficiently influenced, as we have been able to demonstrate, then increasing the probability of conditioning not only can reduce the amount of the sentence actually imposed but reverses a situation, from its equilibrium of high violation, to the its equilibrium of low violation. The results, in addition to the potential they offer to reduce crime and incarceration, can have important implications especially for the correct management of the problem, that of Urban Insecurity.
-
1999
Start of the study on urban deviance phenomena
-
2003
Conception of the predictive model and development of technology and enabling method
-
2004
First experimentation in the city of Naples
-
2012
Creation of the protocol for the use of the solution
-
2013
Academic validation and launch of the framework for placing in operational security offices in six cities
-
2013/2019
Experimentation in operational security offices in Naples, Prato, Salerno, Venice, Modena and Parma
-
2018
SMAU digital innovation award 2018
-
2019
Operational validation of the Central Anti-Crime Department of the Public Security Department
-
2020
Presentation at AIWEEK, the first event dedicated to excellence that makes use of Artificial Intelligence
-
2022
Patent Concession for Industrial Invention
Testing cities involved
For the analysis of the official experimentation, six cities among the eleven have been chosen, which up to now employ technology different in size and socio-urban dynamics.
Napoli
- Surface 117,27 km²
- Population 972.130
- Population density 8.148,22 per km²
- Police Department 1
- Police Office 19
- PCrime 9 (Criminal Pressure Index)
Prato
- Surface 97,35 km²
- Population 185.089
- Population density 2.004 per km²
- Police Department 1
- Police Office 0
- PCrime 9 (Criminal Pressure Index)
Parma
- Surface 260,6 km²
- Population 197.499
- Population density 757,86 per km²
- Police Department 1
- Police Office 0
- PCrime 13 (Criminal Pressure Index)
Salerno
- Surface 59,85 km²
- Population 134.850
- Population density 2,215,89 per km²
- Police Department 1
- Police Office 2
- PCrime 19 (Criminal Pressure Index)
Venezia
- Surface 415,9 km²
- Population 259.809
- Population density 624,69 per km²
- Police Department 1
- Police Office 3
- PCrime 12 (Criminal Pressure Index)
Modena
- Surface 183,19 km²
- Population 186.307
- Population density 1.017,02 per km²
- Police Department 1
- Police Office 2
- PCrime 15 (Criminal Pressure Index)
Goals
Operational effectiveness
Diminished in the cities experience snatches, robberies, thefts and pickpocketing in larger than the national average ed in cities similar in size, number of inhabitants and socio-economic dynamics. The greater effectiveness of the method has been demonstrated forecast compared to the traditional method
Enhancement of human capital
Improve the motivation, participation and ability to make strategic decisions for achieve short and medium goals term by control operators of the territory and operational performance of the entire organization
Savings on safety management costs and for the community
Rationalized the interventions and reduced mileage from patrols, fuel consumption and it stress of men and means. Savings for the collectivity based on the decrease of crimes
Further implications
Operational integration with the others law enforcement - improvement of perception of security and trust in institution by the citizen - improvement of professional reputation from part of the operators - containment of risk factors e of operator stress - scientifically based definition of real safety e perceived - favorable acceptance by the media, academia and law
Analysis method for checking results
QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS
Reduction of crime committed
The number of crimes committed in the cities tested in the year before the trial and in the year in which the trial took place was considered and the results compared with those obtained in other similar cities.Failure to move the crime
The georeferenced distribution of the crimes committed in the year before the trial and in the year in which the trial took place was processed.Effectiveness of the traditional and predictive prevention method
The number of crimes committed was acquired when the traditional and forecasting method was adopted and the difference in results was worked out.Reduction of Km traveled by patrols and wear of vehicles
The number of kilometers traveled by patrols was acquired when the traditional and forecasting method was adopted and the difference was worked out.QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS
Forecast accuracy
The crimes committed and the forecasts processed by the software were compared daily using a special verification tool to assess the reliability and accuracy of the report.Participation of operators
The number of prevention checks carried out on the initiative of operators using the traditional and forecasting method was acquired and the difference was worked out. A questionnaire was submitted to the operators evaluating the solution.Real security and perceived security
In order to verify any differences between real and perceived security, the PCrime (Criminal Pressure) index was considered an integral part of the innovation XLAW® that measures the pressure of crime on the territory in question by virtue of the number of crimes committed in relation to the number of resident and non-resident citizens, the number of homes, businesses, theaters, cinemas, etc., the size of the territory and socio-economic dynamics.Impact on the media and public opinion
The data of interest relating to services were extrapolated and articles offered by the press, TV and web channels.Precision forecast calculations
Through a special verification tool it was possible to evaluate the reliability of the forecasts offered daily by the XLAW® technology.
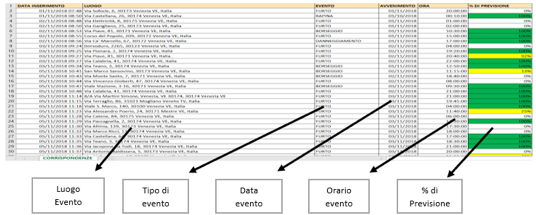
| Experimentation | % Forecast accuracy |
|---|---|
| Napoli | 84% |
| Salerno | 87% |
| Prato | 89% |
| Venezia | 83% |
| Parma | 82% |
| Modena | 86% |
Results
N.B. the results are based on testing by a single police force in six eleven cities that so far employ technologyNapoli
| Prevention results - Overall decrease in crime: 22% | |
|---|---|
| Snatch | -3,9% |
| Robbery | -23,9% |
| Pickpocketing | -5% |
| Thefts in homes and businesses | -12,6% |
| Theft vehicles | -1,6% |
| Criminal Pressure Index | -66,7% |
| Economic results | |
|---|---|
| Savings for citizenship based on prevention results | € 1.555.800 |
| Mileage savings | 61% |
| Fuel savings | € 493.580 |
Salerno
| Prevention results - Overall decrease in crime: 38% | |
|---|---|
| Snatch | -44,2% |
| Robbery | -48,9% |
| Pickpocketing | -19,5% |
| Thefts in homes and businesses | -21,2% |
| Theft vehicles | -1,7% |
| Criminal Pressure Index | -36,8% |
| Economic results | |
|---|---|
| Savings for citizenship based on prevention results | € 801.400 |
| Mileage savings | 47,8% |
| Fuel savings | € 160.300 |
Prato
| Prevention results - Overall decrease in crime: 34% | |
|---|---|
| Snatch | -10% |
| Robbery | -5% |
| Pickpocketing | -21% |
| Thefts in homes and businesses | -10% |
| Theft vehicles | -28% |
| Criminal Pressure Index | -55,6% |
| Economic results | |
|---|---|
| Savings for citizenship based on prevention results | € 522.600 |
| Mileage savings | 40,9% |
| Fuel savings | € 75.920 |
Venezia
| Prevention results - Overall decrease in crime: 19% | |
|---|---|
| Snatch | -23,8% |
| Robbery | -15,5% |
| Pickpocketing | -1% |
| Thefts in homes and businesses | -22,8% |
| Theft vehicles | -24,3% |
| Criminal Pressure Index | -50% |
| Economic results | |
|---|---|
| Savings for citizenship based on prevention results | € 134.800 |
| Mileage savings | 37% |
| Fuel savings | € 54.020 |
Parma
| Prevention results - Overall decrease in crime: 43% | |
|---|---|
| Snatch | -44,2% |
| Robbery | -15,4% |
| Pickpocketing | -5,4% |
| Thefts in homes and businesses | -25,8% |
| Theft vehicles | -30,6% |
| Criminal Pressure Index | -50% |
| Economic results | |
|---|---|
| Savings for citizenship based on prevention results | € 303.800 |
| Mileage savings | 40,9% |
| Fuel savings | € 75.920 |
Modena
| Prevention results - Overall decrease in crime: 16% | |
|---|---|
| Snatch | -6,4% |
| Robbery | -10,1% |
| Pickpocketing | -6% |
| Thefts in homes and businesses | -14% |
| Theft vehicles | -5,9% |
| Criminal Pressure Index | -25% |
| Economic results | |
|---|---|
| Savings for citizenship based on prevention results | € 36.300 |
| Mileage savings | 40,9% |
| Fuel savings | € 68.620 |
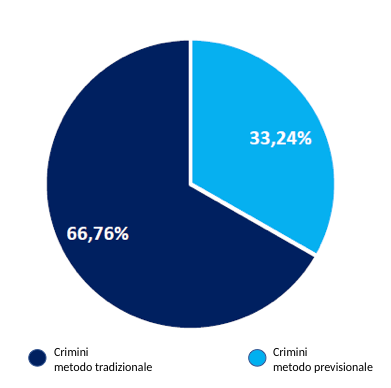
Effectiveness of the forecast method
Crime reduction with the forecast method above the national average and in similar cities
It is common belief that in Italy the reduction of predatory crimes that has been recorded in Italy for some years, can be motivated by several factors including the failure to report by the citizen therefore the doubt that could arise is that the reduction obtained during the experimentation, may possibly be connected to this trend.
Appropriate checks were therefore carried out and the cities tested were compared with those that have the same socio-demographic characteristics, determining that in the cities where the experimentation took place, the reduction in crimes was significantly higher.
| City | % crime reduction (Obtained in the experimentation period) |
N. fewer crimes |
|---|---|---|
| Parma (Experienced city) |
43% | 1.600 |
| Taranto (Untested city) |
19,5% | 577 |
| Salerno (Experienced city) |
38,8% | 642 |
| Ferrara (Untested city) |
4,2% | 192 |
| Venezia (Experienced city) |
19,1% | 923 |
| Catania (Untested city) |
1,8% | 243 |
Effectiveness of the forecast method
Productive difference with traditional and forecasting prevention method
In Italy, control of the territory is shared between two police forces according to a coordinated plan. In the cities you experience the productivity of the one that has adopted the technology XLAW®, was significantly higher, that is, the crimes were committed in greater numbers in the areas of competence of the other force that adopted the traditional prevention method.
During the experimentation, some tests were carried out which provided for the suspension of the use of the technology, verifying that during the suspension the crimes began to increase again and then again to decrease when the technology was used again.
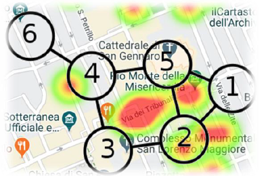
One of the critical points attributed to the forecasting method and to the academic debate center is the possible possibility of moving the crime which in criminology is called "displacement" or one of the risks that criminology attributes in the case of prevention interventions that act on the space or context of the realization of the crime is that the phenomenon moves.
The verification was carried out using diagrams. Starting from a point where the phenomenon was concentrated before the treatment, a diagram was superimposed that unites various points where it would have been possible to move after the treatment based on the morphology and characteristics of the territory.
By virtue of the greater checks carried out on the basis of the alarms generated by the forecast system XLAW®, at the point where the phenomenon was more concentrated (hunting reserve) the only places where it could have been moved are those indicated by numbered circles.
After a year of experimentation the phenomenon has reduced but there has been no movement in any of the alternative points. The verification method was adopted for all the cities where the experimentation took place and for all types of predatory offenses, the result was always the same: the phenomenon has reduced but has never moved.
Participation
Leadership and ability to autonomously make strategic decisions in the short to medium term by local control operators
In the operational offices where the experimentation took place, compared to previous period in which the traditional prevention method was adopted, the checks carried out on the initiative of the operators engaged in control activities of the territory increased daily stimulated by the forecast calculations provided by the systemXLAW®.
A solution assessment questionnaire was submitted to the operators. 100% of the operators interviewed considered the use of the solution useful and motivating, the processing provided by the same for the daily control of the territory was effective, determining the its use for the results that have been achieved, effective in enriching professional skills, simple and inexpensive the protocol for its use perfectly compatible with the existing one.
Impact
Media and public opinion
The use of the XLAW® system thanks to a courageous choice of openness and transparency, has been favorably received by the legal and academic world and has aroused considerable interest from the media which have published numerous press articles and launched numerous television services where the emphasis has always been placed on the innovation adopted, positively affecting the reputation of the institutional brand and the public's feeling of trust towards the institution.
- 261 local press
- 134 nationl press
- 82 international press
- 2.324 Link WEB
- 27 specialized press
- 12.439.000 audit TV 13% share
- 12 local TV
- 15 national Tv
- 12 international TV
Conclusion
XLAW® was born as a secular research project that over the years has embraced several fields of science. With a multidisciplinary approach, each phase of the project was conducted with the contribution of many subjects from the world of public and private security, from the academic world, criminologists, sociologists, urban planners, pedagogues, jurists, computer scientists, economists, doctors and also citizens, especially the active one.
From the beginning, the project was open to anyone wishing to contribute or verify not only the ethical and technological aspects but also the results of the research, study and experimentation of the invention carried out in several contexts where there was no influence of those who has conceived and implemented. Thanks to these courageous ethical choices, the invention is today the only solution in the world of this type that has been transparently put to free judgment and has received the independent consent not only of the experts but also of the academic, legal and public opinion. Unlike many others, often the subject of criticism for lack of transparency, the invention is a White Box and both the user and whoever wants to carry out a serene evaluation, know very well what he has in hand, on what its development is based , what are the principles and purposes of its use, its functioning and what information is collected and considered.
Even if the final outcome of the project has allowed the realization of an innovative technological solution, it is important to underline that it is not correct to define the invention as a technical-IT innovation but the result of a long research activity whose results are an original contribution. for the whole scientific world and for those who intend or still find it difficult to approach similar projects because it has made it possible to shed light on all those gray areas that still arouse skepticism towards new prevention methods to improve Urban Security. First of all, the prevention method based on predictive calculations provided by Artificial Intelligence solutions, was more effective than the traditional method which is based instead on the acquisition of mere statistical reports of past events or on the evaluation of requests formulated by the community. to provide short and medium-term responses that inevitably may come late and that produce poor results and waste of resources. The research carried out, which is made available to anyone wishing to deepen and we also hope to implement, has established that predictive police can be considered reality and no longer science fiction or suggestion.
In fact, the long and widespread experimentation of the invention confirmed the assumption shared by the researchers involved, according to which it is possible to predict certain types of urban crimes that have the characteristic of repeating themselves over time and space, if one is able to to define and implement an appropriate forecasting method and to transfer it to automatic learning models and that the greater the possibility of reducing crimes on the basis of the high reliability and precision of the processing they can provide. Demonstrated and proven that if one is able to predict and prevent crime, it does not move to other areas of the territory, it follows that muggings, robberies, thefts and pickpockets take place in places that are difficult to fungi that if manned with scientific punctuality and precision, it can be made safer by disorienting the criminal who inevitably becomes less effective and more vulnerable in time and space.
It is no coincidence that the project as a whole, in addition to tangible results, has sanctioned sensational upheavals of well-known theories on urban criminology, arousing the attention of the international scientific world.
The framework for the introduction of the invention within a complex organization has been an important success achieved considering that technology must never be an end in itself and that it is not easy to introduce innovation, where working methods are not get ready for this. An exclusive method was therefore studied, developed and adopted with the help of psychologists and technicians to develop a tool that was fully usable, effective and that did not overturn the previous protocols, at a very low cost of installation and management. to be able to affect as much as possible only the performance of the organization and of the individual operators who, thanks to the paradigmatic revolution of the operational objectives and not of the pre-existing working method, were fully proactive and skilled in making decisions from the first hours of adoption of the invention strategic in the daily dispute with the offender.
The conclusion is that the invention should not be considered a further technological resource in addition to the already existing ones but first of all an innovative method that allows to revolutionize the security paradigm to reduce crimes, costs, risks and stress of men and means and the moral and economic damage to the community.
The results, the validation by the Department of Public Security and the Federico II and Parthenope Universities of Naples, the awards, the acknowledgments obtained, the high approval of public opinion and the media and the fact that on the basis of its long experimentation the invention has reached the maximum level of maturity expected that currently nothing similar has reached such levels, determine that the Artificial Intelligence, already used for some time in other sectors, is effective and ready to work daily also in support of activities aimed at making more safe our beautiful cities.
Academic conclusions
Even if at this historical moment Italy is worried about the emergence of other emergencies (effects of climate change, corporate crises, reduction in productivity), the issue of urban security in the country always remains at the top of the institutional agenda, even if a more constant planning of urban security policies is struggling to be realized and the solution of the interventions lend themselves to easy exploitation, both from the right and from the left.
However, it cannot be denied that security represents a fundamental good of the person, a recognized universal right of the person (Article 3 Universal Declaration of Human Rights) and as such is considered by our Charter among "the inviolable rights of man" (Article 2 of the Italian Constitution), for which as such it is payable because without it freedom cannot be exercised and without this any human activity can be prosecuted and expressed in all its greatness. Therefore, security should be managed continuously, beyond the party line-up.
Security, justice and freedom are interconnected values: without security there is no freedom and justice cannot be guaranteed either. However, safety is both an objective condition (guaranteed by a set of safeguards and devices) and subjective, as it relates to the person's state of mind, his psychological condition, so much so that this dimension is studied through the perception of 'insecurity. When the State fails to guarantee security, autonomous training courses are proposed in history as alternatives to offer safeguards, protection, guarantees. The mafia originates historically precisely as a social subject that offers protection in the absence of the state. It is sold to the point that Franchetti in 1876 in the famous "Inquiry" identified the mafia as experts in the use of violence to protect property rights that were weakly or not at all safeguarded by the state.
The lack of security feeds fear and paradoxically advanced modernity, being pregnant with new risks, instills a greater sense of general insecurity because it makes many living conditions more precarious and what once were habitual certainties vulnerable. However, since there is a very close relationship between security and inequality, those who live on the lower rungs of the social ladder are objectively more vulnerable as they are less protected and consequently the perception of insecurity is a function of the weaker status. Those who are placed, on the other hand, in the upper steps enjoy greater guarantees, equip themselves with greater self-protection and for them the sense of insecurity is nourished more by subjective elements or those aspects of contemporary life that are connected to global risks (pollution, terrorism , large migratory flows, economic crises) instill anxOne of our local specificities is that, unlike other contexts such as the United States, England or France itself, urban security programs have never been crossed by strategic experimentation of models centered on the prevention of events and attention to victims in a delimited urban space. This has happened more frequently abroad under the aegis of programs implemented by active police departments in collaboration with universities, mayors or government offices. The New York period of "zero tolerance" (from 1990 to 2001) implemented especially by Rudolph Giuliani (1994-2001) it would be wrong to translate and identify it in an exclusively political key. This would prevent us from grasping some analytical insights and insights that, starting from the studies of the social psychologist P. Zimbardo at the end of the 1960s on "collective indifference" and from the subsequent theories of "broken windows" (Broken Windows Theory, Kelling and Wilson , 1982), of the "social contagion" (Cook and Goss, 1996) and of the hypotheses connected to the Moving to Opportunity (MtO) programs (Harcourt - Ludwig 2006), have allowed us to grasp some social effects connected to and / or induced by the degradation and urban disorder.
The criticisms leveled at the Safe and Clean Neighborhoods programs and even more at the zero tolerance strategies have instead given rise to a long period of experimentation coinciding with the foot-patrol, community policing, problem-oriented policing programs, which although of little effectiveness or not giving the desired results (Jang et alii, 2008) they were superimposed by other applied models (“pulling levers” policing, third-party policing, hot spots policing, compstat and evidence-based policing) to prevent crime or to counter it. Especially after 11 September 2001 when answering the citizens' security question became an absolute imperative. Rather than retreating, the many critical issues that have emerged in recent years with respect to the different experiments have consolidated the search for new ways in the USA, testing the results of the application of new strategies and enriching the correlation models between factors in order to provide more reliable answers. (Taylor, 2001; Nixon 2005; Braga et alii, 2014). Insiders and scholars of the field debate on the one hand, making clear the idea that a good deterrence is built by pursuing both minor infractions and violent crimes, even if the approach to the type of crime present in a given area. Fear, disorder, the development of crime are in any case connected to both small infringements and violent crimes whose side effects end up discouraging interest and participation in the defense of the community. On the other hand, those who believe that criminalizing incivilities and any form of soft crime is a mistake, a waste of resources and an ineffective way of countering the sense of insecurity of the community, even if collecting inadequate results on the crime front (Braga et alii, 2015). Even increasing the number of street agents or making sentences harder and longer does not have an effective deterrent effect on those who choose the path of crime (Paternoster, 2010).
The study behind this project takes into account how the theme of urban security, although it requires integrated social and economic interventions, redevelopment of public spaces, environmental design and incentives for citizens to participate in the care and defense of the thing. public, is based primarily on the application of territorial control strategies by the more organized police forces. Reformulated on the basis of previous criminological analyzes capable of simulating future situations.
The Federico II University of Naples has accepted to collaborate in the project because for years a close comparison has been developed on the use of operational and predictive security models and the XLAW® model, poses serious questions to the theory of contagion (which also includes illustrious thinkers: G. Le Bon; S. Freud; N. Smelser) and to the psychology of collective behavior whose results were then extended to the mathematical theory of the spread of diseases used by epidemiologists to predict the course of infections within a population (NTJ Bayley, 1957).
The results that the model produces are located exactly in that progressive itinerary that has shifted attention from irrational processes to rational and intentional ones studied in the context of the theories of the transmission of beliefs and information within the stock markets (A. Lynch 1998, 2000; RJ Shiller 2000) and who are powerfully revolutionizing new criminology by crossing, among other things, the results that derive from environmental design and victimization research.
We must take XLAW® seriously, the result of teamwork and an institutional synergy that has crossed different knowledge, experiences and skills, the results of which crack one of the assumptions that are popular for some: building security by militarizing the territory. Nothing more false. The predictive urban security activity offers more effective results expected to combine research, technology and criminological reflexivity.
In fact, XLAW® collects information on the basis of a selective hypothetical theoretical construct which, although inspired by rational models (integrates the theory of opportunities by PM Mayhew, R. Clarke et alii, 1976; the theory of rational choice by DB Cornish and RV Clarke , 1986; the theory of criminal geometric spaces by PJ Brantingham and PL Brantingham, 1991; the theory of routine activities by M. Felson and L. Cohen, 1979; crime mapping, victimization findings), goes further both because it refutes , as anticipated, some aspects of the reaction-diffusion models of predatory crimes connected to the formation of hot spots and therefore to the displacement effect, both because it shows the temporal character - it does not exclude it - relative to the reconstruction of the "hunting reserve". This puts the police in a position to anticipate the moves (prevention) by disrupting the conditions that give rise to the event. An evaluative selection, therefore, of the criminogenic factors that with high probability determine the cases, building a risk assessment model based on the logic of the use of "big data".
Situational prevention is enriched because the selection of information that the XLAW® model tends to incorporate does not concern itself with reducing opportunities, but assumes that it is the hunting reserve (with its own characteristics) that must be modified and observed, waiting for the its infungibility (or reconstruction of analogous properties).
Is it transferable to other contexts?
Is it transferable to other crimes (displacement other crime)?
The assumptions about seriality, specialization, modus operandi and the type of victim defined tell us that it is possible. This is the challenge that should be accepted. Certainly the operating modality and tenacity - not common - of those who conceived and promoted the project shows how important and opportune is the updating and specialization of the local police bodies, even of the police forces, stabilizing in paths of comparison the academic world, experts and those experimenting with new models of criminal analysis or new territorial control strategies.
XLAW® shifts the strategic construct of control action from a restorative view of the damage to a probabilistic view of risk. So from a logic of "running after" problems and the effects they generate (typical of permanent emergency) to one that works on prevention schemes.
Such an operational proposal must be considered. Results are offered that restore operational effectiveness, enhancement of human capital, new knowledge, savings on management costs, additional hypotheses of action with other law enforcement agencies. And that's not cheap!
- Prof. Giacomo Di Gennaro Department of Political Sciences Director of the II level Master Criminology and Criminal Law Criminal Analysis and Policies for the Urban Security Federico II University of Naples)
Bibliografia, Sitografia e Media
Bettoni R., Lombardo E., Piccoli D., Sicurezza Urbana: questione pubblica e privata? Urbanistica Informazioni n.286, INU Edizioni, ISSN 0392-5005, Anno XXXXVI, Luglio-Agosto (2019), p. 67
Di Gennaro G., Lombardo E., Marselli R., Spina M. (2018) Tolleranza zero o deterrenza selettiva - Secondo Rapporto Criminalità e Sicurezza a Napoli. FedoaPress, University Federico II, Naples.
Di Gennaro G., Lombardo E., Riccio G., Ruffolo U., Uricchio A.F. Intelligenza artificiale e politiche di sicurezza urbana: verso quali modelli?" Cacucci editore (2020) ISBN 9788866119685
Di Gennaro G., Lombardo E. Intelligenza artificiale e politiche di sicurezza urbana: verso quali modelli? ISBN 9788866119685
Lombardo E. " Intelligenza Artificiale e Human Intelligence per prevenire i crimini" - Società Italiana Intelligence (2020) Press ISBN-13 (15) 979-12-80111-03-6 - DOI (06) https://doi.org/10.36182/2020.11
CNR " L’Intelligenza Artificiale per lo Sviluppo Sostenibile" Progetti dal mondo XLAW Pag. 113 e 196
Fondazione Leonardo - Civiltà delle macchine Umanesimo digitale" Polizia predittiva e Smart City vecchie e nuove sfide per il diritto penale
Thomas R. Criminologia minorile. Un approccio sostenibile. Giuffrè (2020) ISBN 9788828819004
Sicurezza 4P Perchè la Polizia Predittiva per la Sicurezza Urbana in Italia ha funzionato
Claudia Morelli giornalista professionista esperta di Diritto e Diritti per ALTALEX (2019): Furti e rapine - a sventarli ci pensa l’intelligenza artificiale!
Michele Iasselli Avvocato, docente di logica ed informatica giuridica presso l’Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II. Docente a contratto di informatica giuridica presso LUISS - dipartimento di giurisprudenza per ALTALEX (2018): XLAW la polizia predittiva è diventata realtà
Riccardo Coluccini per Motherboard Tech by Vice (2018): La Polzia predittiva in Italia è diventata realtà e non ce ne eravamo accorti
Candido Romano per Business Insider (2019): XLAW l'algoritmo che prevede scippi rapine furti e funziona da anni
Francesco Santin per Drcommodore (2018): XLAW il futuro italiano della polizia predittiva
Parmateneo università degli studi di Parma (2018): Predire il crimine non è più fantascienza. A Parma arriva XLAW
Parma Press: “Sicurezza – Arriva a Parma XLAW, il software che prevede dove e quando avverrà un crimine
Parma Press: “Grazie a XLAW Polizia ferma possibili ladri nel San Leonardo: tre rumeni già segnalati per furti
Reggio Sera: “Minority report” è realtà, arriva l’algoritmo che prevede i reati
Madi Ferrucci per TPI (2019: XLAW l’algoritmo che prevede i furti e le rapine in base a un modello matematico
Roberto Tomas già magistrato minorile-docente di criminologia del Master di criminologia presso la Sapienza-Università di Roma per Polizia Penitenziaria (2019: L'algoritmo XLAW che prevede dove e quando sarà commesso un reato o La criminalistica e l'algoritmo XLAW che prevede i reati
Ministero dell’Interno: In azione anche a Sassuolo il sistema preventivo – predittivo recentemente introdotto dalla questura di Modena, XLAW
Il Denaro: Poliziotto napoletano idea l’algoritmo che prevede i reati: sperimentazione a Modena
Dal sito Polizia di Stato Venezia: Venezia: i reati vengono previsti da un algoritmo
Dal sito Polizia di Stato Modena: XLAW le nuove strategie messe in campo dalla Polizia di Stato per il controllo del territorio
Dal sito Polizia di Stato Modena: Grazie al software XLAW, la Polizia di Stato mette a segno un altro risultato: arrestato in flagranza un topo d’appartamento
Dal sito Polizia di Stato Parma: XLAW è il nuovo modo di fare controllo del territorio da parte dell’UPGSP della Questura di Parma
Dal sito Polizia di Stato Venezia: Venezia-Mestre. Arrestati per furto due cittadini romeni. Il sistema XLAW strumento vincente
PSB Privacy e Sicurezza : XLAW, l’I.A. che contrasta il crimine
Il Tirreno: Prato reati in calo con XLAW
Premio SMAU: Casi di successo XLAW l'algoritmo poliziotto che prevede i crimini
Corriere della sera: Attenti al ladro l'annuncio lo fa il software XLAW che aiuta la Polizia ad arrestare i criminali
Roma: Napoli poliziotto digitale anticipa i ladri e le loro mosse una denuncia
Modena Today: Algoritmo XLAW della Polizia per prevenire i crimini a Modena
Modena Today: Polizia modenese adotta XLAW, software che prevede reati predatori
Ansa: XLAW APP Questura anticipa un furto
Il resto del carlino: La questura presenta il software che prevede i reati
Il resto del carlino: Polizia, un altro arresto grazie al software XLAW
Tvqui Modena: Polizia di Stato arrestato malvivente grazie al nuovo software XLAW
Il denaro: XLAW sbarca a Venezia software made in Napoli per prevenire i reati urbani
Parma daly: Operazione antidroga della Polizia col sistema predittivo XLAW
Venezia Today: Prevenire i reati grazie a XLAW, sistema che ottimizza il lavoro della polizia
Il Gazzettino Venezia: XLAW funziona, il software che "prevede" i furti coglie un ladro sul fatto
Repubblica: Parma in Questura arriva il software che prevede i crimini
Focus Polizia Penitenziaria: L'algoritmo XLAW che prevede dove e quando sarà commesso un reato
Gazzetta di Parma: Polizia impegnata nei controlli con il sistema XLAW che predice i reati
Pisa Today: Pisa qualità della vita usiamo XLAW
Il Riformista: I ladri li possiamo anitcipare con la tecnologia
Securindex: XLAW il sistema predittivo contro i reati predatori
Fanpage: A Napoli la Polizia prevede i crimini con XLAW
Il Mattino: Napoli sistema elettronico XLAW prevede un furto arrestato l'autore
Il Giornale: Venezia ecco software che predice i reati
Business Insider: Un algoritmo che prevede i crimini e funziona da anni
Rai la Vita in Diretta: Lotta al crimine ecco la tecnologia che batte i ladri
Motherboard: Polizia predittiva XLAW l'algoritmo per prevedere i crimini
Ansa: XLAW app della questura anticipa furto
Sul Panaro: XLAW ora i ladri li cattura l'algoritmo
Mediterranei news: Giornata mondiale del Turismo e Festival dell’Ospitalità XLAW per la sicurezza dei turisti
105.net: Inventato algoritmo per prevedere furti e rapine prima che si verifichino
Stylo24: XLAW l'algoritmo che prevede i crimini
Internapoli: Prevenire il primo convegno sulla Predictive Policing a Napoli
SIAP FOCUS: Innovazione strategica e tecnologia per la prevenzione dei reati
La Verdad: El oráculo del delito: Así se puede predecir dónde se va a producir un delito
DECA Human Resurces: Furti e rapine a sventarli ci pensa l'intelligenza artificiale
El Pais: El policía que aprendió a programar para predecir crímenes
El Financiero: Cuando Minority Report nos alcanzó
Repubblica: XLAW l'algoritmo che batte i ladri
Globo: Polícia usa algoritmo que prevê crimes para prender ladrão na Itália
ELCIERRE Digitla: Un inspector napolitano creò un algoritmo con capacidad para precir los movimientos de los ladrones antes de que actùen
Spain's News: The policeman who learned to program to predict crimes
Televisiva News: El ladrón que fue atrapado en Italia gracias a un nuevo algoritmo para predecir delitos inventado en Nápoles
Espacio Arms: XLAW Algoritmo Policia Predictivo
Automating Society Algorithm Watch: Automating Report 2020: Italy
Gazzetta di Parma: Controlli straordinari in città. Denunciato un 19enne sorpreso a rubare a Mediaworld
Parma Report: Operazione antidroga vincente grazie al sistema XLAW
Metropolitano: Più sicuri con XLAW i furti si possono prevenire
Il Riformista: I ladri? Li possiamo anticipare con la tecnologia
Bologna 2000: In azione anche a Sassuolo il sistema preventivo – predittivo XLAW
Bologna 2000: Un altro arresto a Modena grazie al software XLAW
Patto sicurezza urbana Roma Capitale art.5: XLAW nel Patto per la Sicurezza Urbana di Roma Capitale
Il Riformista: Napoli, è allarme sicurezza: per vigilare usare la tecnologia
Assemblea Camera dei Deputati seduta n.90 del 26.11.2018 Intervento dell'On. Alessio Butti: Molto interessante, l'algoritmo antifurti, denominato XLAW
Ristretti dal Il Fatto Quotidiano: "XLAW": un algoritmo può davvero prevedere (e impedire) un reato?
Civile On Line: Un altro arresto della Polizia di Stato grazie al nuovo software XLAW
Venezia Today: Cercano di rubare una moto, ma gli agenti erano già lì grazie a XLAW: arrestati
Storie Polizia Penitenziaria: Quando per il bene del paese opera l'appartenente al corpo con uniforme e mostrine e non un civile che nulla sa dell'operatività di un corpo di Polizia, le cose funzionano
Press Reader: Via Bissuola ore 12:00 prevista rapina dall'algoritmo che guida le volanti
Modena Today: Prevedere il crimine e anticiparlo, la sfida dell'intelligenza artificiale della Polizia
Bologna2000: Un altro arresto a Modena grazie al software XLAW
Tv Qui: A Modena arriva XLAW per predire i reati
Gazzetta di Modena: XLAW, l’algoritmo anticrimine dà i primi frutti anche a Modena
Tv Qui: Polizia di Stato, arrestato malvivente grazie al nuovo software XLAW
Dire: A Parma arriva un ‘cervellone’ per predire i reati
Privacy e Sicurezza: XLAW, l’I.A. che contrasta il crimine
Business Insider: Percezione o realtà? I danni della paura e i dati reali per contrastarla
Napoli Today: La polizia napoletana prevede i furti: due denunce grazie all'app XLAW
El Confidencial: El ordenador 'atrapaladrones': este es el algoritmo que predijo un robo en Italia
Dagospia: L'algoritmo che predice i reati come minority report si chiama XLAW
Telecapri News: Napoli l'app XLAW della questura blocca uomo con attrezzi da scasso denunciato dagli agenti
Parmateneo: Predire il crimine non è più fantascienza. A Parma arriva XLAW
La Nuona Procedura Civile: Automanting Society Report 2020: Italia avanti con Polizia e Giustizia Predittiva
Polizia di Stato: Attività di controllo straordinario del territorio della Polizia di Stato per il contrasto allo spaccio di sostanze stupefacenti e ai reati predatori in generale
Il Mattino: Sistema di X-Law, a Napoli preso 38enne dopo una rapina
Polizia di Stato: Controlli straordinari del territorio della Polizia di Stato 3 denunciati ed un daspo urbano
LUMSA News: Crimine zero, la sfida del poliziotto che prevede il futuro
Il Riformista: XLAW funziona, ora investire per salvare Napoli dalla criminalità
Prefettura di Napoli: Devianza grave minorile XLAW allo studio della Prefettura
La Repubblica Parma: Parma, in questura arriva il software che prevede i reati
Salvi Juribus: I sistemi di Intelligenza Artificiale in uso alle Forze dell'Ordine in Italia
Gazzetta dell'Emilia: Arrestato grazie al programma di previsione dei reati XLAW
Sassuolo 2000: Un altro arresto a Modena grazie al software XLAW
Modena Today: Polizia modenese adotta XLAW, software che prevede reati predatori
Press Reader - Gente: La nuova tecno-arma della Polizia
Parmareport: Operazione antidroga vincente anche grazie al sistema XLAW
Safety e Security Magazine: Sicurezza Urbana – Dopo le formalità è tempo di concretezza operativa
Centro Studi Livatino: Le frontiere giuridiche dell'Intelligenza Artificiale
L'Opinione: Le frontiere giuridiche dell'Intelligenza Artificiale
State of Mind: Prevedere un reato è possibile? XLAW tecnologia all’avanguardia si pone come modello predittivo di illeciti di tipo predatorio
Segni dei tempi: Città sicure con XLAW, l’algoritmo della polizia. Sperimentazione anche nella provincia di Napoli
Salvi Juribus: I sistemi di intelligenza artificiale in uso alle Forze dell’Ordine in Italia
Repubblica: Parma, in questura arriva il software che prevede i reati
Domani: Anche in Italia è arrivata la “polizia predittiva” per fare sicurezza urbana
Altalex: XLAW, il brevetto italiano di polizia predittiva
Lab Parlamento: Dimmi dove vivi e ti dirò che crimine ci sarà: così anche la polizia diventa predittiva
Piùsicurezza: Polizia Predittiva per la sicurezza urbana:Sistema made in Italy
Edicola WEB: L’algoritmo-anti rapina in soccorso della Polizia
MEDIASET MATRIX: XLAW a MATRIX
RAI: Primi riscontri a Napoli dopo la sperimentazione di XLAW
IL SERRAGLIO: XLAW a Napoli per strategie innovative contro il crimine
RAI regionale: A Napoli XLAW la tecnologia innovativa contro i crimini
RAI regionale: XLAW a Napoli prosegue la sperimentazione
TV PRATO: XLAW a Prato i primi risultati della sperimentazione
RAI TG1: Anche a Venezia XLAW non fallisce
TG VENEZIA: XLAW nella città lagunare
A3 NEWS Venezia: Venezia primo arresto grazie a XLAW
RAI Mimanda RAI 3: XLAW e la Polizia di Stato a Mi Manda Rai 3
RAI Uno in famiglia: XLAW e la Polizia di Stato a Rai Uno In Famiglia
SMAU report premio innovazione digitale: Premiazione SMAU 2018
RAI Italia Si: XLAW sul podio di Italia Si Rai Uno
Gazzetta di Modena: La Questura di Modena presenta XLAW
Polizia di Stato Parma: Parma presentazione XLAW
RAI Tg3 Emilia: A Parma e Modena si sperimenta XLAW
Tg Parma: Il sistema predittivo XLAW sventa furti in appartamento
Gazzetta di Modena: Polizia, XLAW l' "arma" della polizia che prevede furti, scippi truffe e rapine
RAI La vita in diretta: XLAW la tecnologia che batte i ladri
La Nuova Venezia: XLAW, l'aiutante tecnologico della Questura di Venezia
TG Venezia: Un sistema matematico in grado di prevenire i reati predatori. E' arrivato nella questura di Venezia
Rete Veneta: Primi risultati di XLAW. Il sistema adottato in questura, a Venezia, in grado di prevedere i reati predatori

